What Is Hydraulic Lifts?
A hydraulic lift is a device that can lift objects, based on the force developed in lifting equipment by a liquid acting under pressure in a cylinder and moves a piston upwards.
In we put oil into the cylinder which is incompressible and moves up until we loose control and open the valve so we can get the piston moving downward by gravity.
These lifts operate using Pascal’s Law. Pascal’s Law states that any change in pressure in an incompressible fluid in a confined and closed space is transmitted equally throughout the liquid in all directions.
Pascal’s Law in hydraulic systems can be demonstrated when you apply a small force on an incompressible liquid on one end while a large force is applied on the other end.
Hydraulic systems can provide controlled and precise force and motion, they are a cost effective option, and they are a capable use of energy.

Key Takeaways
- The hydraulic lift exerts a force to move an object using the force of pressure on the liquid in a cylinder that moves a piston upward.
- The function and principle for hydraulic lifts is based on Pascal’s law to create force or motion on a object to lift, which states that if a pressure change on any incompressible liquid in a closed space, the pressure is transferred equally throughout the liquid in all directions.
- Hydraulic lifts preform controlled and precise force.
- Hydraulic lifts have been popular in a number of industries for their fundamental simple design that is strength based and structural confining durably.
- The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) have specific regulations regarding hydraulic lifts and operator training.
- Lift tables have gained popularity as a form of work surfaces which can be adjusted to the precise height required for packaging, assembling, organizing or positioning materials.
How do Hydraulic Lifts Work?
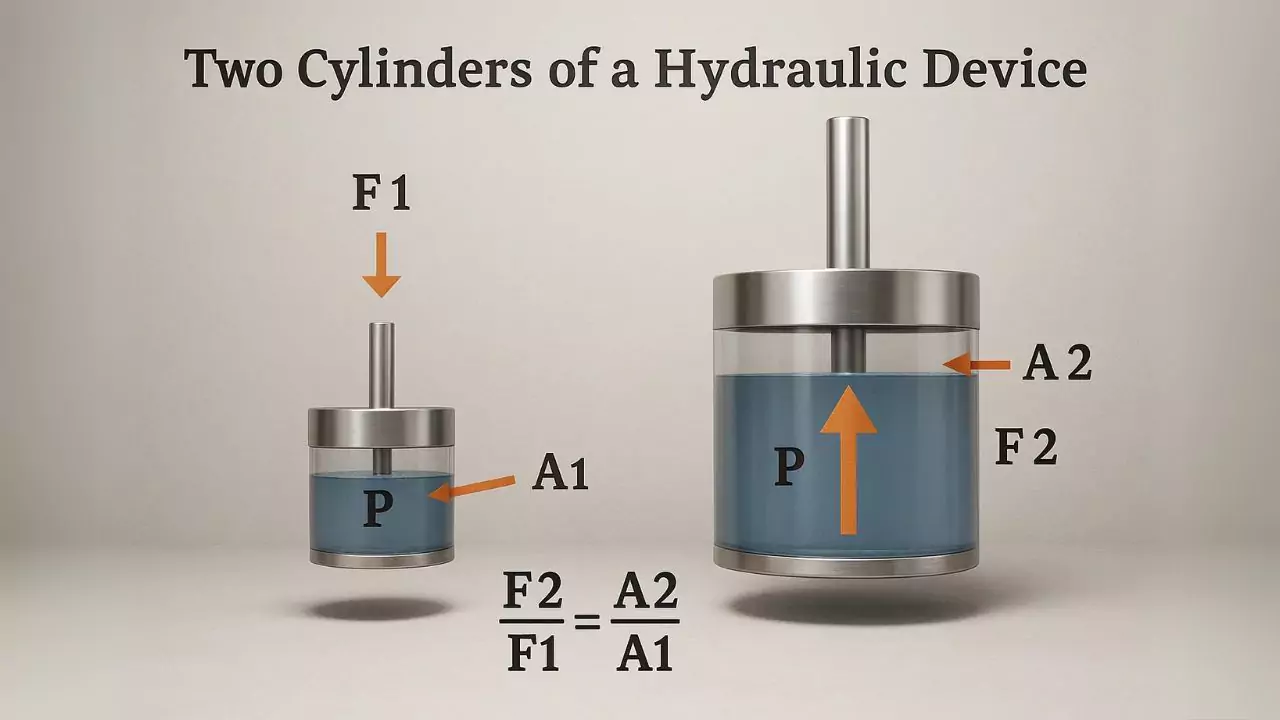
A hydraulic system operates by applying force to an incompressible liquid. The force, or “pressure,” is then transferred to a second location, or piston. A hydraulic system consists of two pistons connected by a pipe filled with oil.
The following image shows the two pistons connected by a pipe.
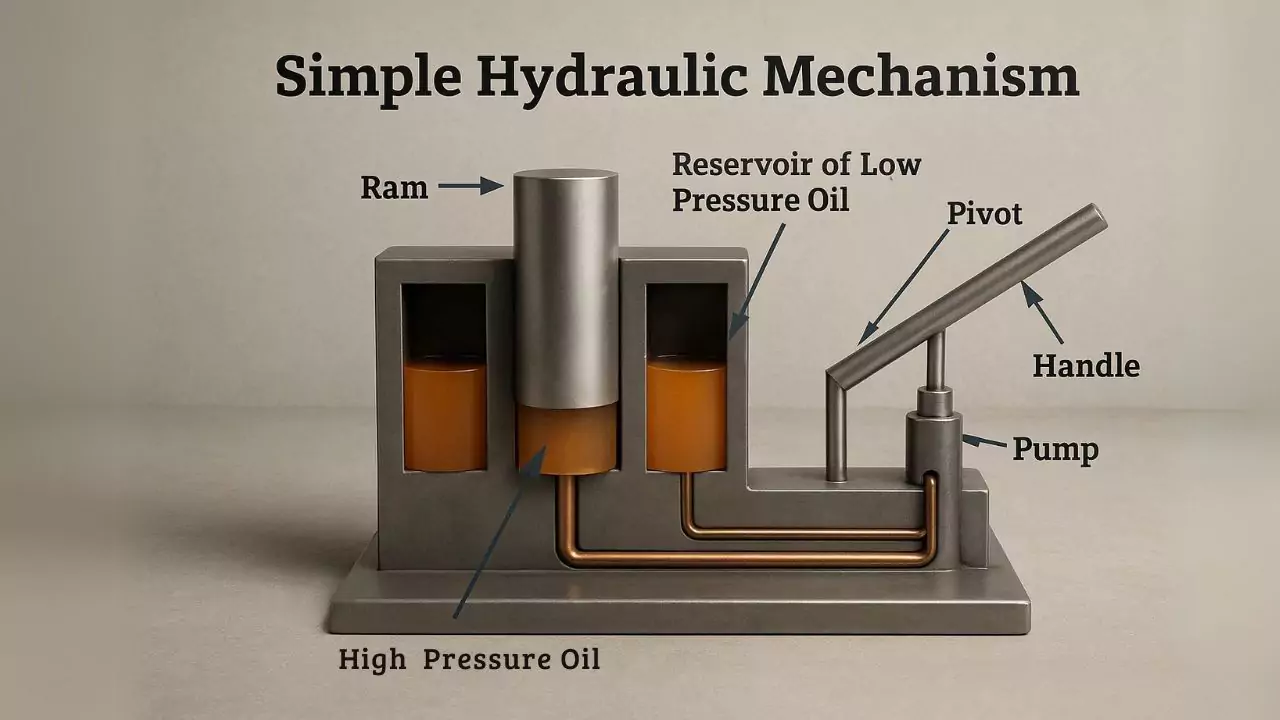
The image below shows a typical hydraulic device mechanism. The handle located on the right is pumping incompressible oil from the reservoir into the high-pressure chamber at the mid-point of the drawing. As the oil is pumped into the chamber, the ram encountered by the ram rises.
Force Generated
The amount of force generated in a hydraulic system is dependent on the size of the pistons. If the smaller piston is two-inches in size, and the larger piston is six inches in size (e.g., three times larger), then the amount of force produced will be nine times larger than the smaller piston. For example, a small piston generating a force of 100 pounds can lift 900 pounds.

In the image above, the smaller piston has a weight of one pound and a one square inches area. If this piston travels downward by ten inches, it will generate enough force to lift the ten-pound load on the larger piston to the right.
Parts of a Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system has multiple applications and usage, but the concepts and components of hydraulic systems are the same. Like any hydraulic system, the most important factor of that hydraulic system is the hydraulic liquid (fluid).
As we know from physics, the pressure being applied to the liquid remains constant during the transfer of that pressure throughout the hydraulic system. Below is a description of each individual parts element of a hydraulic system.
Hydraulic Circuits
Hydraulic circuits provide control over the flow and the pressure of the liquid in the system. Below is a simple representation of a hydraulic circuit.
Hydraulic Pump
A hydraulic pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. The pump creates a vacuum at the inlet of the pump which allows liquid to be drawn out of the reservoir to fill the inlet line and the hydraulic system through the outlet.
Hydraulic Motor
A hydraulic motor is an actuator that uses hydraulic pressure to produce torque and produce motion (rotational). A hydraulic motor converts hydraulic energy with pressure and flow into rotational mechanical energy just like a linear actuator converts hydraulic energy to linear motion.
Once hydraulic energy from the pump is supplied to the motor, the motor can produce mechanical energy in the form of rotational force.
Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder converts energy from hydraulic fluid to force. It exerts pressure onto the hydraulic fluid as controlled by the hydraulic motor.
Hydraulic Pistons
Hydraulic pistons go through linear displacement due to fluid pressure. Furthermore, axial pumps consist of several hydraulic pistons arranged in a circular configuration which allows to act on a rotating housing.
Hydraulic Fluids
Hydraulic fluids transfer power in a hydraulic system. Hydraulic fluids are usually either mineral oil or water. Water was the original hydraulic fluid; mineral oil was adopted in the twentieth century.
For hydraulic applications requiring high temperature resistance, or fire safety other fluids can be considered, including glycol ether, organophosphate esters, polyalphaolefins, propylene glycol, and silicone oil.
Types Of Hydraulic Lifts
In their various forms hydraulic lifts have become mission-providing technology for various industries. Any application that assists people being ambulatory, or providing individuals with accessibility for boarding buses, is an essential technology.
The versatility of hydraulic lift technologies have exploded in its applications and markets in just the last few years.
Following are descriptions of different types of hydraulic lifts.
Table lifts
Table lifts elevate an object from the floor to a working height. Transportation companies like Humers use hydraulic lift tables to elevate materials up onto a truck bed or a warehouse floor.
Personnel lifts
Personnel lifts allow users to safely elevate people to reach working heights, such as for repairing electrical lines, the placement of inventories on shelves, or accessing control panels.
It’s not uncommon to see personnel lifts within a gymnasium, a factory, or entertainment venues. Often people elevate employees for cleaning of lights and ceilings.
Fork lifts
Fork lifts allow users to transport materials throughout construction sites, warehouses, and factories; and loading and unloading from trucks and airplanes. Fork lifts are useful for elevating materials from one place to another.
Medical lifts
Medical lifts maintain surgical tables, hospital beds and monitoring equipment at an adjustable height. Hospital beds with hydraulic systems assist staff in moving patients from their rooms to treatment locations.
The hydraulic feature allows staff, patients, or caregivers similar to nurses to raise or lower the beds to achieve the best height for accessibility as well as patient comfort.
Automotive lifts
Automotive lifts are designed to lift vehicles for repair and visual inspection. Automotive lifts are some of the strongest hydraulic lifts available. This is due to the heavy loads (cars and trucks) they are designed to lift.
Post car lifts
Post car lifts are a type of automotive lift. Car is raised between the two post and the car is raised by four arms on hydraulic drives. Any type of vehicle can be lifted with a post car lift.
Platform lifts
Platform lifts, or elevated work platforms, are like lift tables but larger and designed to carry groups of workers with their equipment or tools. They serve as a large platform with an elevation to carry out various elevated tasks.
Pallet lifts
Pallet lifts are used for shipping / material handling. They are like a fork lift in that they can lift pallets from the ground floor of a building to load the truck, rest a pallet on a shelf, or carry material to production lines.
Hand pumped lifts
Hand pump lifts employ a manual hydraulic hand pump, and have a release lever that lowers the load. These lifts have a long useful life and afford the least amount of maintenance. Hand pumps can lift up to one ton to a height of more than six feet.
Custom Hydraulic Lifts
The manufacturers of hydraulic lifts recognize every industrial application is unique and requires custom engineering solutions, so they also offer custom hydraulic lifts for specialized, unique, A hydraulic lift can be manufactured, constructed, and configured for specific circumstances or environments.
Some of the variables that can be adjusted include:
- Frame dimensions
- Lift strokes and stroke speed
- Safety (e.g. explosion proof materials, lock-up bars)
- Custom materials ( laminates, ESD lining, stainless steel)
- Multi-axis rotation
- Having different options for height adjustability
- Other attachments ( forks, clamps, shelving, tables, seating)
All hydraulic lift manufacturers have engineers that can customize and adjust their lifts to suit various industrial and manufacturing applications.
As new developments and conditions occur, it is likewise important that hydraulic lifts have a degree of flexibility in the way they can be modified, adjusted or redesigned to keep up with the fast past of industrial requirements.
Vertical Reciprocating Conveyor (VRC)
Vertical Reciprocating Conveyors (VRC), also referred to as vertical material lifts, freight lifts, and conveyor lifts, are defined by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) as “conveyors and related equipment” under their ASME B20.1 definition.
VRC’s are designed to ONLY move materials are not designed to move people. VRC’s can be installed inside buildings and outside of buildings to move materials in all shapes, sizes, and weight between floors, mezzanines, balconies, basements, and the multiple levels of multi-storied buildings.
VRC’s have more versatility in placement options than elevators. They do not need separate machine rooms or feet of pit depth making them more efficient in terms of footprint.
VRC’s have structural supports and enclosed carriages that make it impossible for the load to fall out which makes them a much safer and efficient alternative to forklifts or scissor lifts.
A VRC consists of the guide column, the carriage and the hydraulic activating device. The VRC’s can either be mechanical or hydraulic, with hydraulic VRC’s rated to carry loads ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 pounds above the floor.
A hydraulic VRC system is typically less expensive to install compared to its mechanical counterpart. The VRC system is best in applications where there are two levels to access and there is a lifting range from 25 ft. or less, and there is no requirement for continuous cycle operation.
Configurations
- Straddle: The carriage slides between guide columns where force is applied vertically in the longitudinal direction of the beams.
- Cantilever: The carriage can be accessed in three directions and is located in front of the guide columns.
What are hydraulic lift tables
Lift tables are being utilized more and more as work surfaces that can be positioned at the exact height required when performing tasks such as packaging, assembling, organizing, or positioning items.
Hydraulic lift tables are different than adjustable tables, as lift tables lift at a much higher load rating than typical adjustable tables.
Conventional lift tables have lift capacities for loads between 2,000 up to 6,000 pounds and have a low setting of 7 inches and a high setting of 60 inches.
The normal workspace for a lift table is 24 to 72 inches. Lift tables are available in many shapes and sizes to fit many applications. Below is a brief description of some of the different types of lift tables.
Mobile
Mobile lift tables, or lift carts, are also a push cart that can be raised with a manual foot pump. They are typically employed for light assembly tasks and provide the luxury of mobility.
Rotating Hydrualic Lift Tables
Rotating hydraulic lift tables are lift tables with a turntable that is recessed into the surface; this allows access to a load from all four directions. The turntable utilizes anti-friction bearings to rotate, for both easy and smooth operation.
The turntable can be locked in place when not in use. Rotating hydraulic lift tables can be low-profile types that can be lowered to a very close distance from the floor (a few inches or so) which makes them accessible with a pallet jack or a fork truck.
Like all hydraulic tables, rotating hydraulic lift tables are constructed with materials that are heavy-duty, and can lift near a ton of product.
They were created to position loads in a specific manner that reduces the reliance on a worker to manually lift, and increases energy savings related to overall operations.
Low Profile Lift Tables
Low-profile hydraulic lift tables have a collapsed height of a few inches, which enables them to be loaded using a hand truck or a fork truck. They do not need a pit, or indentation, so they can also be used on upper floors, as well as main floors.
All low-profile hydraulic lift tables raise and lower via a foot switch, or a push button remote that enables the operator to raise and lower the table, to the optimum working height.
Low-profile tables are designed to; provide ergonomic positioning of loads for, easy handling/unloading, reduce worker fatigue, augment productivity, and overall improvement of work satisfaction. They can be used in a variety of applications due to their adjustability.
Stainless steel
Lift tables manufactured from stainless steel are frequently used in the food and pharmaceutical sectors because these sectors adhere to very high hygienic and sanitary requirements.
Stainless steel will not corrode or rust and can be easily cleaned with solvents and water; therefore, they comply with the requirement for cleanliness.
High Capacity Hydraulic Lift Tables
High capacity hydraulic lift tables are heavy-duty machines with the ability to carry loads up to 60 tons in weight and lifting heights up to 52 to 92 inches. Typically, their standard platform size is from 4′ x 6′ to 10′ x 22′, and they can be made in custom larger sizes.
High capacity hydraulic lift tables have scissor legs and torque tubes that provide superior support, stability and extremely low load deflection or shifting.
The amount of scissor legs and hydraulic cylinders will vary depending on the lift table’s make and design model. High capacity hydraulic lift tables, like all hydraulic tables, can be operated via handheld pendant control or foot switch, and contain an upper travel limit switch.
Additional items can also be added like tilt tops, powered turntables, V-cradles and corrosion resistant finishes.
High capacity hydraulic lift tables are specially designed and specified to fulfill the demand and constant usage that heavy-duty machinery encompasses, therefore they are the true workhorses of the lift table family.
Ground Entry Lift Tables
Ground entry lift tables are specifically designed platform lifts as ground-level access to its platform enables opportunity to address tripping hazards or space constraints. They are fitted with a ‘U’ or ‘E’ shaped cut-out area to facilitate loading when using open bottom pallets or skids.
Tilting Lift Tables
Tilting lift tables provide enhancements for use in handling containers which contain free parts. Once raised to an ergonomic height, these tables will tilt towards the operator reducing the demands on bending/stretching.
The tilting tables allow for adjustment directly to a maximum tilt of 90 degree, to ultimately provide greater accessibility and ease of use.
Tandem Lift Tables
Tandem lift tables comprise the installation of standard lift functions with additional lifts to increase the length or width of the lift platform. This concept obviously provides incrementally larger benefits on utilising more of the lift platform area and enhances the table’s edge and side load capacities.
Multi-Stage Lift Tables
Multi-stage lift tables utilise two stacked pairs of scissor arms. The extreme example of two mounted lift tables layered on top each other. This provides mechanical advantage through longer vertical travel and the ability to reduce the platform size.
Applications of hydraulic lifts
Hydraulic lifts include some steel and have meaningfully precise accuracy such that they are strong and durable and can used across industries and applications. As perspective, here are some industries in which hydraulic lifts are applied and are also most efficient performance.
Industrial
The application of electro-hydraulics is the most common use of hydraulic technology in many industry settings. Some of the key strengths in hydraulics are the rapidity of response and high accuracies.
Hydraulic systems are utilized in a multitude of applications across a variety of industries; plastic processing, metal extraction, automated factories, machine tools, paper manufacturing, loaders, crushers, presses, textiles, etc. Figure below shows a hydraulic press used in the plastics industry.
Mobile Hydraulics
Mobile hydraulics offer the adaptability to change with different conditions and environments. They are widely used in the construction and building industries; cranes, excavators, backhoes, and earth moving equipment are only some examples.
Automobiles
The automotive industry uses hydraulic technology more than any other industry. Hydraulics are used in manufacturing, repair, and in many internal components of the vehicles they manufacture.
Marine Applications
Marine hydraulics offer linear and rotary force and torque rapidly and which are efficient. The three marine hydraulic system types are open, closed, and semi-closed.
Marine hydraulic systems are used for cranes, mooring and anchor winches, stabilizers, steering, thrusters, propellers, and platforms.
Aerospace Applications
Aerospace components have to meet strict standards before they are approved for service. Hydraulic pumps and valves are very important to meet these standards, and they play a very important role in aircraft design and construction.
Hydraulics are used for wing movement, landing gear retract and extend, door movement, brakes, and steering.
Mining
Hydraulics are the most suitable force application for mines due to their power, controllability, reliability, and ease of maintenance, particularly in a dangerous area. Not only are mines industrial operations, they involve mines, and more significantly industrial size operations and equipment.
There are few forces that can deliver this amount of power and force. This makes hydraulic systems ideal for the mines due to all of the operational forces involved in mining.